In today's rapidly evolving electronics landscape, the demand for efficient and reliable electronic designs has never been higher. Among various technologies, rigid printed circuit boards (PCBs) have emerged as a critical component, offering numerous advantages that cater to modern design requirements. According to a report by TechNavio, the global rigid PCB market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% from 2020 to 2025, reflecting the increasing reliance on these essential elements within a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to automotive systems.
Industry expert Dr. Jane Smith, a leading figure in PCB technology, highlights the significance of rigid PCBs, stating, "The robustness and structural integrity of rigid PCBs make them indispensable for high-performance electronics." This sentiment is echoed across the industry, as manufacturers and designers recognize that rigid PCBs provide not only enhanced durability but also improved thermal management and better signal integrity. Furthermore, their ability to accommodate complex designs makes them ideal for miniaturized devices, a trend that continues to shape the future of electronic innovation.
As we delve into the top five benefits of using rigid PCBs in modern electronic design, it becomes clear that these components play a vital role in meeting the expectations of efficiency, reliability, and performance in an increasingly competitive market.

The miniaturization of electronic devices is revolutionizing the electronics industry, with rigid PCBs playing a crucial role in driving efficiency and reliability. Rigid PCBs are designed to accommodate smaller components and complex circuitry, making them ideal for modern applications where space is at a premium. Their ability to support intricate layouts allows designers to create compact electronic solutions without sacrificing performance.
As industries push towards smaller and more efficient products, the demand for rigid PCBs continues to grow. For instance, the copper-clad laminates market is forecasted to increase significantly, reflecting the rising need for high-quality materials that support miniaturization. Similarly, the rigid flex PCB market is experiencing substantial growth, particularly in regions like China, where the demand for flexible and space-efficient design continues to escalate. This trend underscores the significance of rigid PCBs in facilitating technological advancement and innovation across various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices.
Rigid PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) have emerged as a cornerstone in modern electronic design, particularly due to their enhanced thermal management capabilities. One of the primary benefits of rigid PCBs is their ability to dissipate heat more efficiently than other board types. In high-performance applications where heat can significantly impact functionality and longevity, rigid PCBs are engineered with materials that promote superior thermal conductivity. This reduces the risk of overheating, ensuring that sensitive components operate within safe temperature ranges.
Additionally, the structured design of rigid PCBs allows for better thermal distribution across the board. By implementing strategic layout techniques and utilizing thermal vias, engineers can channel heat away from hot spots and maintain a balanced temperature throughout the device. This is particularly vital in compact electronic devices where space is at a premium. Ultimately, the enhanced thermal management capabilities of rigid PCBs not only safeguard the reliability of electronic systems but also contribute to overall performance, making them an indispensable choice in contemporary electronics design.
| Benefit | Description | Impact on Design |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Thermal Conductivity | Rigid PCBs can dissipate heat efficiently due to their constructed materials. | Allows for higher component density and reduced risk of thermal damage. |
| Improved Stability | Rigid PCBs maintain their shape under thermal stress. | Ensures reliable performance in demanding environments. |
| Better Layer Registration | High precision in layer alignment thanks to rigidity. | Reduces issues related to misalignment and improves signal integrity. |
| Reduced Weight | Utilizing lightweight materials without compromising rigidity. | Aids in designing portable electronic devices. |
| Cost-Effective Mass Production | Streamlined processes for large quantities. | Lowers overall manufacturing costs for businesses. |

Rigid PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) offer significant cost-effectiveness that appeals to manufacturers and designers in the modern electronic landscape. Their stable structure allows for efficient mass production, resulting in lower per-unit costs compared to flexible or other types of PCBs.
This economic advantage becomes particularly pronounced when producing large quantities of electronic devices, where the initial investment in tooling and setup can be amortized over many units. Additionally, the materials used in rigid PCBs, such as FR4, are relatively inexpensive, further driving down manufacturing costs.
In terms of long-term reliability, rigid PCBs excel due to their robustness and durability. They resist warping and bending, leading to better performance in high-stress environments. This stability ensures that electronic components maintain secure connections over time, reducing the risk of failures that can lead to costly recalls or repairs.
Moreover, advancements in manufacturing techniques have boosted the quality and precision of rigid PCBs, enabling them to withstand thermal and mechanical stresses while maintaining functionality.
As a result, manufacturers can expect fewer failures and a prolonged lifespan for their products, making rigid PCBs a strategic choice for modern electronic design.
Rigid PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) have become increasingly popular in modern electronic design, especially due to their role in enhancing signal integrity and minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI). With the demand for reliable and high-performance devices, the importance of effective signal transmission cannot be overstated. Rigid PCB technology ensures that signals travel along well-defined paths, reducing the chances of distortion and data loss. This is critical in applications ranging from telecommunications to medical devices, where signal clarity is paramount.
To further improve signal integrity, designers should consider optimizing trace width and spacing. Maintaining proper dimensions can significantly reduce the risk of crosstalk and interference between adjacent tracks. Additionally, utilizing ground planes can create shielding that absorbs stray EMI, thereby ensuring that the signals remain pure and intact.
When designing rigid PCBs, it’s also beneficial to analyze the layout with simulation tools. These tools can predict potential signal degradation and interference issues before the manufacturing process, allowing for proactive adjustments. Ensuring that components are strategically placed can minimize the path length for signals, further enhancing overall performance. Ultimately, taking these steps can lead to more reliable and efficient electronic designs, capitalizing on the inherent advantages of rigid PCB technology.
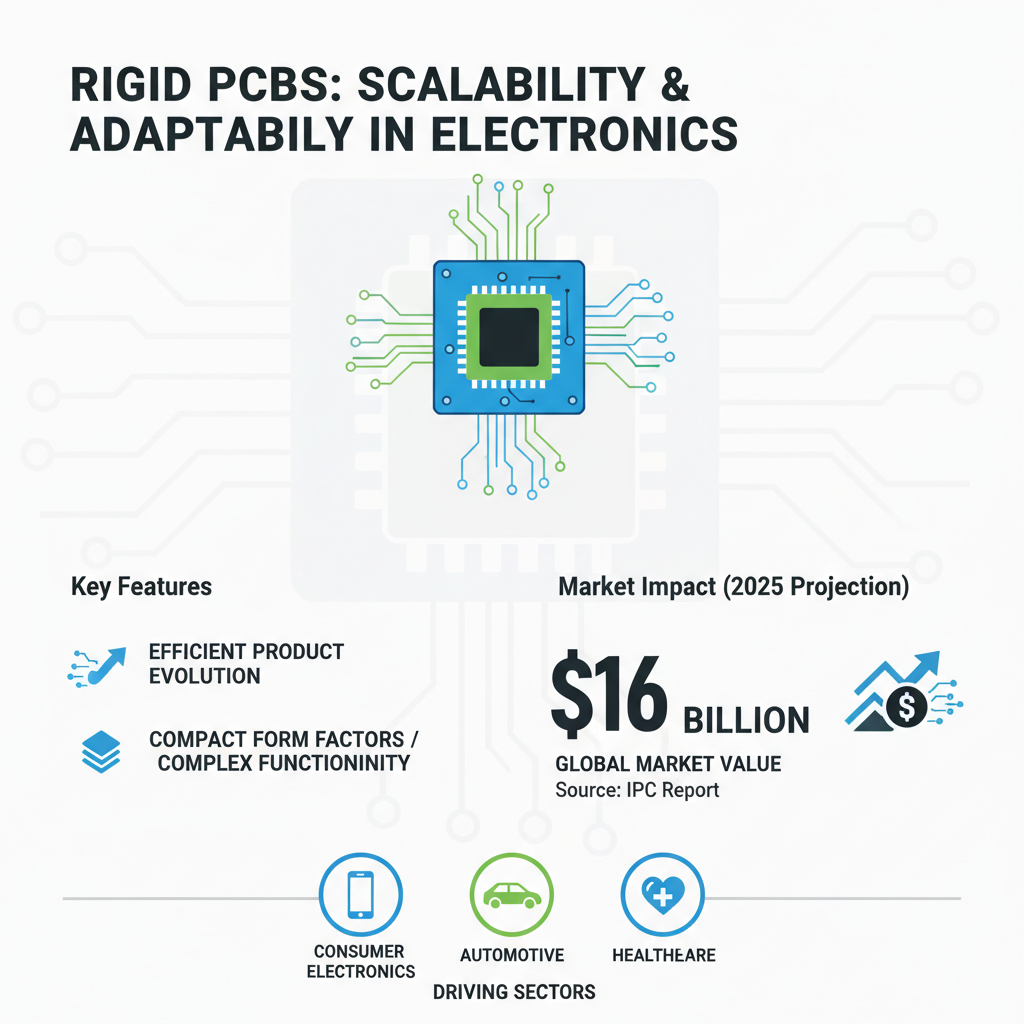
The scalability and adaptability of rigid printed circuit boards (PCBs) play a crucial role in modern electronic design, allowing products to efficiently evolve alongside technological advancements. According to a report by the IPC (Institute of Printed Circuits), the global rigid PCB market is expected to reach $16 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing demand for reliable and scalable solutions in various sectors including consumer electronics, automotive, and healthcare. This growth is driven by the need for high-performance electronics that can support complex functionalities while maintaining compact form factors.
In today's fast-paced development environment, rigid PCBs offer significant design flexibility, accommodating diverse applications from smartphones to smart appliances. Their ability to integrate multiple layers and components enables engineers to create more sophisticated devices with enhanced capabilities. A study from Research and Markets points out that the demand for high-density interconnection (HDI) designs in rigid PCBs is rising, which in turn facilitates faster data transfer rates and improved power efficiency. This adaptability not only caters to current technological requirements but also provides a robust platform for future innovations, ensuring that manufacturers remain competitive in a rapidly changing marketplace.