In the ever-evolving landscape of electronics, the demand for innovative solutions is driving designers to explore advanced technologies. Rigid flex rigid PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) have emerged as a transformative solution, combining the benefits of both rigid and flexible circuit technologies. According to renowned industry expert Dr. Emily Chen, "Rigid flex rigid PCBs provide unparalleled versatility, allowing for more compact designs without compromising on reliability." This insight underlines the growing significance of rigid flex technology in meeting the needs of modern applications.
As projects become increasingly complex, the advantages of rigid flex rigid PCBs are hard to ignore. They offer reduced weight, increased durability, and enhanced performance in a range of applications from consumer electronics to medical devices. The ability to create intricate geometries and minimize assembly time has made rigid flex an attractive option for engineers and designers seeking efficiencies in their production processes. By integrating these capabilities, projects can achieve higher quality and innovation, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in electronic design.
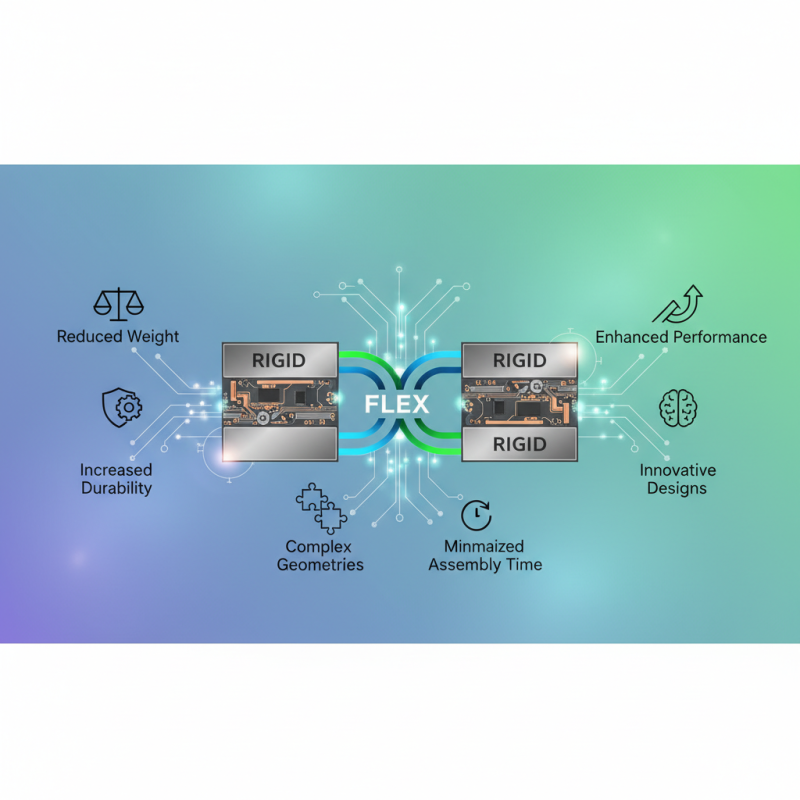
Rigid flex rigid PCBs offer a multitude of benefits in modern electronics design, making them an increasingly popular choice among engineers and designers. One of the most significant advantages is their ability to save space and reduce the overall weight of electronic devices. By combining the strengths of rigid and flexible circuits, these PCBs enable designers to create compact and lightweight solutions that can fit into tight spaces, which is vital for portable electronics like smartphones, wearables, and other consumer gadgets.
Another key benefit of rigid flex rigid PCBs is their enhanced durability and reliability. These PCBs are engineered to withstand mechanical stresses and environmental challenges, such as vibration and temperature fluctuations, which can lead to failures in traditional circuit boards. The seamless transition between rigid and flexible areas allows for more robust connections, reducing the risk of fractures and enhancing the lifespan of the electronic device. Additionally, the reduced number of interconnections required means fewer solder joints, further minimizing potential points of failure and improving overall performance.
When considering the design and functionality of printed circuit boards (PCBs) for modern electronics, the comparison between rigid flex rigid PCBs and traditional PCBs reveals significant advantages. Traditional PCBs, while widely used, typically consist of a single rigid substrate that can limit design versatility. Their inflexible nature restricts assembly options and can lead to increased space requirements in compact devices. In contrast, rigid flex rigid PCBs combine the best of both worlds by integrating flexible circuitry with rigid components, enabling a more innovative approach to device design.
The benefits of rigid flex rigid PCBs extend beyond mere space-saving capabilities. These hybrid boards enhance durability, as they are less prone to damage from bending or vibration, making them ideal for portable electronics that endure constant movement. Additionally, the streamlined assembly process, which can be achieved through fewer interconnections and improved ease of integration, reduces potential failure points. This reliability and efficiency can significantly lower production costs over time, making rigid flex rigid PCBs a compelling choice for engineers seeking to push the boundaries of technology in their next project.
Rigid flex rigid PCBs have gained significant traction across various key industries due to their unique ability to provide enhanced performance and reliability in complex applications. The aerospace and defense sectors, for instance, are increasingly utilizing these advanced circuits for their lightweight and high-density capabilities. According to a report by the IPC Association Connecting Electronics Industries, the aerospace industry alone is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5% through 2026, with rigid flex PCBs playing a crucial role in miniaturizing components while maintaining operational integrity in demanding environments.
In the medical device industry, rigid flex rigid PCBs are transforming product designs by enabling compact configurations that meet stringent regulatory standards. A recent study indicates that the global medical PCB market is expected to reach $3.1 billion by 2025, driven by the need for smaller, more efficient devices. The integration of rigid flex technology allows for intricate routing while resisting mechanical stress, leading to improved durability and reduced risk of failure in life-critical applications such as diagnostic equipment and surgical tools.
Electronics consumer goods are another sector where rigid flex rigid PCBs are becoming increasingly popular. As devices demand greater functionality in smaller footprints, manufacturers are turning to these advanced interconnect solutions to achieve innovations in smartphones, wearables, and IoT devices. Research from Markets and Markets predicts that the flexible PCB market will reach $28 billion by 2024, highlighting the urgency for high-performance, space-saving designs. This trend underscores how rigid flex technology not only enhances product performance but also creates new possibilities for design and functionality in various applications.
| Industry | Application | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Devices | Portable Monitoring Equipment | High density, flexible design | Improved diagnostics, compact size |
| Aerospace | Avionics Systems | Temperature resistance, lightweight | Enhanced reliability, fuel efficiency |
| Consumer Electronics | Smartphones and Tablets | Space-saving design, durability | Sleek form factor, longer lifespan |
| Automotive | Infotainment Systems | Shock resistance, high vibration tolerance | Enhanced safety, superior user experience |
| Industrial | Automation and Control Systems | Robust design, customizable | Increased efficiency, reduced space |
Rigid flex rigid PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) are increasingly becoming the go-to choice for many industries due to their unique blend of cost efficiency and longevity. These innovative circuit boards combine the best features of rigid and flexible PCBs, allowing for intricate designs without sacrificing durability. This hybrid structure not only reduces the need for additional connectors and interconnects, leading to lower assembly costs, but it also enhances the overall reliability of the product in demanding applications.
Moreover, the longevity of rigid flex rigid PCBs is a significant advantage for projects requiring a robust solution. Their design minimizes the risk of mechanical failure and wear, which often plagues traditional circuit boards, particularly in dynamic environments where space is limited. By reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance, businesses can enjoy substantial savings over the lifetime of their products. This durability, combined with the cost-effectiveness of production, makes rigid flex rigid PCBs an ideal choice for companies aiming to maximize their return on investment while delivering high-quality electronic solutions.
This chart illustrates the comparison of cost efficiency and longevity between rigid flex rigid PCBs and traditional PCB solutions over a project lifecycle. The data reflects benefits such as reduced assembly time, material savings, and increased durability.
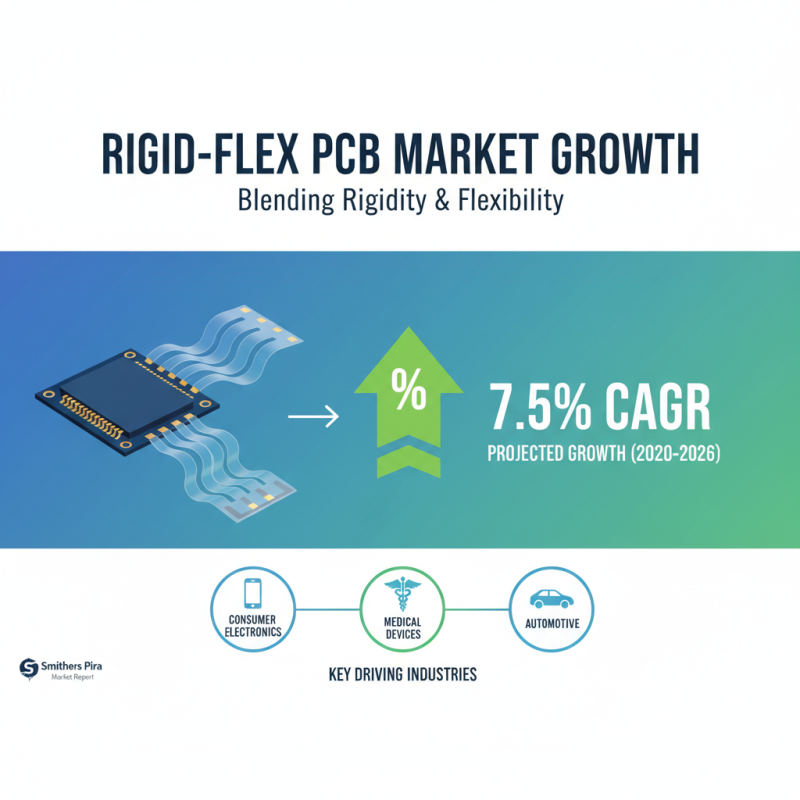
Rigid flex rigid PCBs have become increasingly popular in various industries due to their unique combination of rigid and flexible features. These PCBs typically integrate multiple layers that consist of both rigid and flexible materials, allowing for greater design freedom and compact configurations. According to a market report by Smithers Pira, the global rigid flex market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.5% through 2026, driven by demand in consumer electronics, medical devices, and automotive applications.
When considering the technical specifications for rigid flex rigid PCBs, understanding the industry standards is crucial. IPC-2223, the standard for flexible printed boards and rigid-flex printed boards, outlines the design, manufacturing, and reliability requirements for these circuits. Compliance with such standards ensures that the products are durable and reliable under varied environmental conditions. Moreover, the thickness of the flex circuit layers can range from 0.5 to 3.0 mils, with rigorous testing like thermal cycling and bend testing recommended to validate performance against potential mechanical stresses.
Furthermore, the material selection for rigid flex PCBs focuses on low-loss dielectrics to enhance signal integrity, especially in high-frequency applications. Materials such as polyimide and FR-4 are commonly used due to their excellent thermal stability and mechanical properties. It's essential for design engineers to refer to the most updated specifications provided in the IPC standards to optimize product performance while adhering to industry norms.