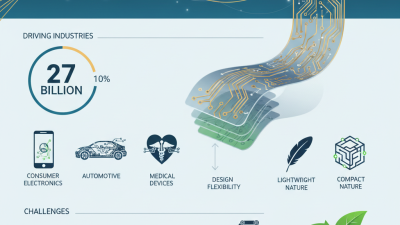
In the rapidly evolving world of electronics, flex PCB manufacturing plays a crucial role. According to market research from IPC, the flexible circuit market is expected to reach $12 billion by 2025, highlighting its increasing significance. Industry expert Dr. Jane Smith emphasizes, "Understanding the nuances of flex PCB manufacturing can significantly affect product longevity and performance." This insight underscores the importance of careful planning and execution in this specialty area.
Many companies overlook essential practices in flex PCB manufacturing. For instance, material selection can make or break circuit reliability. Issues like improper lamination can lead to costly failures. A recent survey revealed that 30% of manufacturers face challenges due to inadequate quality control measures. Reflecting on these pitfalls is essential for innovation and growth in this sector.
Moreover, as devices become smaller and more complex, the demand for flexible circuits continues to rise. Flex PCBs enable a reduction in size without compromising functionality. However, achieving high-quality results requires a disciplined approach to design and production. As the industry evolves, it’s clear that mastery in flex PCB manufacturing is not just an advantage; it's essential for survival.
Flex PCBs, or flexible printed circuit boards, are revolutionary in the electronics industry. Their unique characteristics include flexibility, lightweight design, and the ability to be molded into various shapes. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, flex PCBs can bend and twist, making them ideal for compact and dynamic applications. This adaptability opens doors for innovative designs in devices like smartphones, medical equipment, and wearables.
When considering the manufacturing of flex PCBs, attention to detail is crucial. Ensure proper material selection for flexibility without compromising durability. Thin materials can lead to breakage, especially during assembly. A delicate balance is necessary here. Design for manufacturability is another tip; complex designs can lead to costly errors. Simplicity often enhances reliability.
Testing your designs is essential. It can catch potential issues early on, saving time and resources. Collaborate closely with your manufacturing team. Open communication can lead to better outcomes. Flex PCBs have immense potential, but the road to success requires careful planning and execution. Always be prepared to refine your approach based on feedback and lessons learned.
| Tip | Description | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Understand Material Choices | Choose appropriate substrates based on application needs. | Improved performance and reliability. |
| 2. Design for Flexibility | Optimize PCB layout for bending and compression. | Reduced risk of cracking and failure. |
| 3. Utilize Proper Layer Stacking | Group layers strategically for strength. | Enhanced durability and performance. |
| 4. Consider Assembly Techniques | Select appropriate soldering and assembly methods. | Improved manufacturing efficiency. |
| 5. Test for Reliability | Implement rigorous testing protocols. | Identify potential failures early. |
| 6. Select Efficient Manufacturing Partners | Collaborate with experienced flex PCB manufacturers. | Optimized production processes. |
| 7. Understand Cost Implications | Evaluate material and fabrication costs. | Improved budgeting accuracy. |
| 8. Focus on Advanced Techniques | Stay updated with new manufacturing technologies. | Increased competitive edge. |
| 9. Document All Processes | Maintain detailed records of design and production. | Facilitated troubleshooting and quality assurance. |
| 10. Collaborate with Engineers | Engage cross-functional teams in design reviews. | Improved design outcomes. |
When designing a flex PCB, layout considerations play a crucial role in ensuring functionality and reliability. Flex PCBs are unique due to their ability to bend and twist. Therefore, it’s essential to prioritize the placement of components. Avoid clustering components too closely. Adequate spacing reduces stress and potential damage during flexing.
One common mistake in layout design is neglecting the width of traces. Traces that are too narrow can lead to issues with current capacity. Wider traces can improve conductivity and decrease resistance. Furthermore, consider using vias wisely. They are important for connecting layers, but too many vias can increase the risk of failure. Each via adds weight and can be stress points.
It’s also vital to simulate the flexing and bending of the PCB. This helps identify any weak points in the layout. Sometimes, designs that look perfect on paper fail in real-world tests. Proper analysis can reveal areas needing reinforcement. Flexibility must be balanced with durability. Testing iterations can lead to better outcomes. Keep learning from each design cycle; improvement is an ongoing journey.
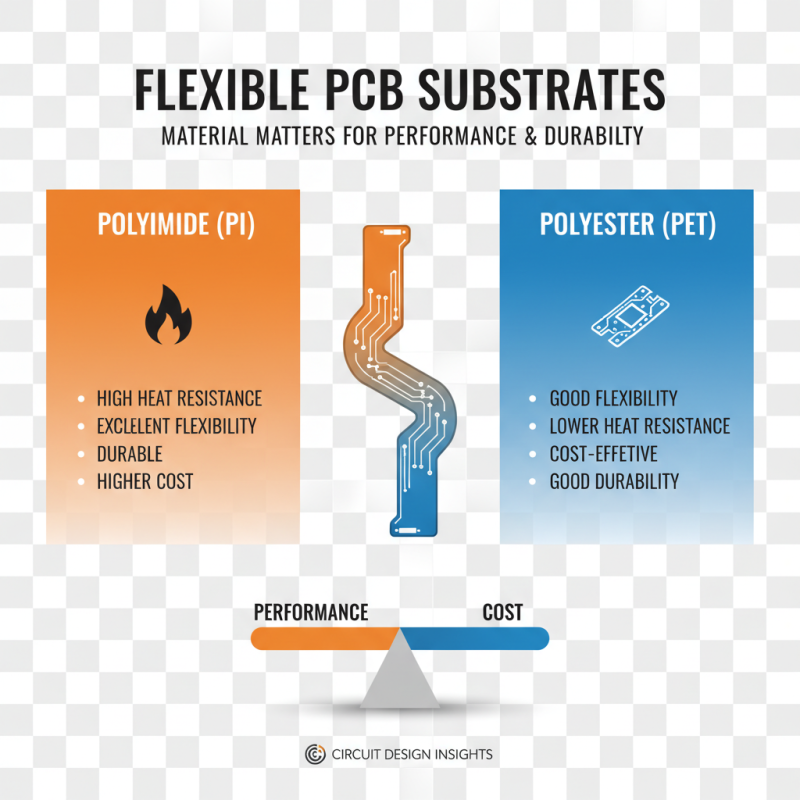
When selecting substrates for flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs), material choice is critical. The right substrate can influence the board's functionality and durability. Polyimide and polyester are popular choices. They offer exceptional flexibility and thermal resistance. However, these materials can vary in price and performance.
Tip: Always assess the application needs before making a choice. Consider the environment and temperature ranges. Are you working with wearable technology? The substrate must withstand bending and stress. Test small batches to ensure they meet specifications.
Another key factor is the thickness of the substrate. Thinner materials provide better flexibility. However, they may be more prone to damage. On the other hand, thicker substrates can offer enhanced durability, but at the cost of flexibility. Balancing these attributes can be challenging.
Tip: Don’t overlook the coating options. They can impact both protection and flexibility. A good coating can enhance the substrate's performance. Conducting thorough tests can help identify the best combination. Remember, an ideal solution today may not work tomorrow.
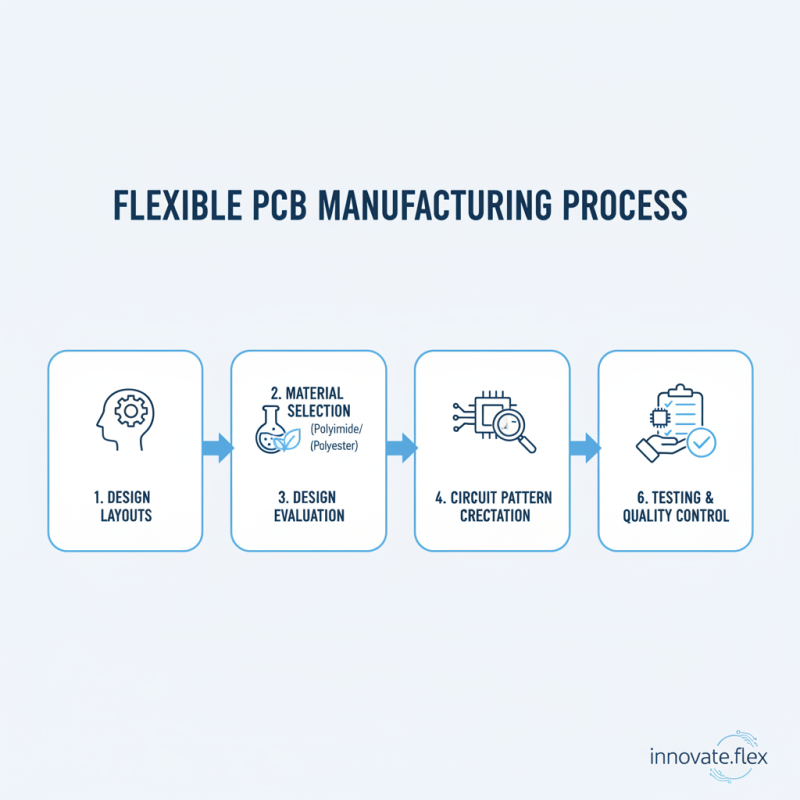
The manufacturing process of flexible PCBs involves several crucial steps. It starts with design considerations. Engineers must create precise layouts for the circuit patterns. Choosing the right materials is paramount. Polyimide or polyester films are common choices. These materials allow flexibility and durability. Each design must be carefully evaluated.
Once the design is complete, it's time to move to film generation. Photomasks are produced to define the circuit layout. This step can be tricky. Errors in this phase can lead to significant issues later. Afterward, the circuit is etched onto the substrate using chemical processes. Accuracy is critical here. A small mistake can compromise the entire board.
The next phase involves applying additional layers. This can include adhesives and protective coatings. Each layer must bond well with the previous one. Quality control during this stage is often neglected. Yet, it’s vital to ensure reliability. Once completed, the boards undergo electrical testing. Not all flex PCBs pass this stage. Identifying flaws before distribution saves time and resources. Adjustments may be necessary based on these results.
Quality control is vital in flex PCB manufacturing. It ensures that the final product meets specific standards. When issues arise, they often lead to performance failures. A small error in design can result in significant consequences. Testing and inspection processes must be robust and thorough to catch these mistakes.
Visual inspections play a crucial role in quality assurance. Operators should meticulously check for defects in the layout. Equipment calibrations are equally important. Misalignments can lead to poor performance. Regular audits of manufacturing processes can identify inefficiencies. These audits should not just be routine; they must actively seek areas for improvement.
Documentation should be clear and accessible. Teams need to understand what constitutes a successful product. Failure to communicate specifications can lead to misunderstandings. Engaging with the team about potential flaws encourages a culture of quality. Mistakes are valuable learning tools, urging teams to reflect and improve continuously. Emphasis on education and training helps in fostering a quality-driven environment.