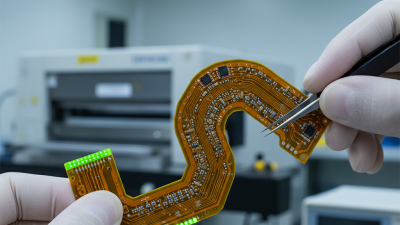
Flex PCB assembly plays a crucial role in modern electronics. This technology allows for a compact and efficient design. As devices become smaller, traditional PCBs struggle to fit. Flex PCBs offer a solution to this problem. They are lightweight and can conform to various shapes.
In consumer electronics, flex PCB assembly enhances performance. A smartphone's internal structure relies on this technology. Flexible circuits enable advanced features with minimal space. However, not all manufacturers utilize flex PCBs effectively. Some face challenges in production and design.
The demand for innovation pushes companies to adopt flex PCB assembly. Yet, issues like durability and heat resistance must be addressed. Continuous improvement is needed in the industry. Balancing flexibility with reliability is crucial for progress. Flex PCB assembly is vital, but it requires thoughtful implementation.


In modern electronics design, flex PCBs play a pivotal role. These printed circuit boards are lightweight and adaptable, making them ideal for various applications. According to industry reports, the global flexible printed circuit board market is expected to reach $20 billion by 2025. This growth showcases the demand for innovation in electronics.
Flex PCBs are particularly valuable in compact devices, such as smartphones and wearables. Their ability to bend allows for intricate designs in smaller spaces. Studies indicate that these assemblies can reduce weight by up to 75%. However, designing flex PCBs is not without challenges. Engineers must balance flexibility with durability to ensure reliability.
Another consideration is manufacturing complexity. Producing flex PCBs requires advanced technology and precision. Mistakes in the design phase can lead to costly errors. Ensuring the reliability of these boards under stress remains a crucial focus. As the demand for smaller, more efficient devices increases, the importance of flex PCB assemblies will continue to rise.
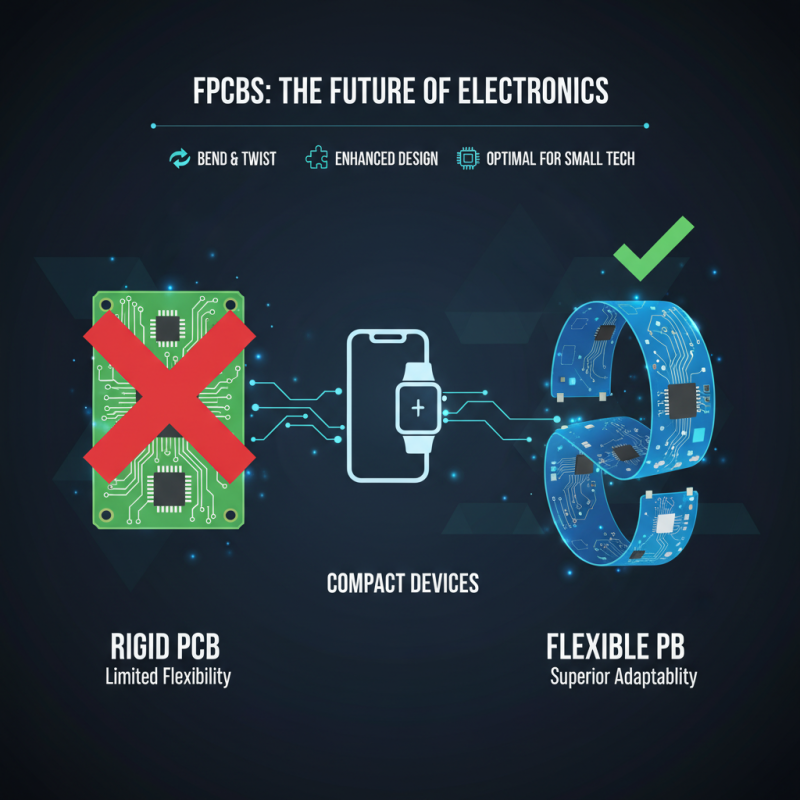
Flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs) are gaining traction in modern electronics. These boards offer superior adaptability. Compared to traditional rigid PCBs, FPCBs can bend and twist without losing functionality. This unique characteristic enhances design versatility, especially in compact devices.
According to market research, the flexible PCB market is expected to reach $20 billion by 2025. This reveals a shift toward flexible solutions in industries like consumer electronics and medical devices. FPCBs also save space. They can be integrated into smaller enclosures, allowing for more innovative product designs. The ability to fit complex circuits into tight spaces is crucial in today's tech landscape.
Manufacturing costs for FPCBs can pose challenges. The production process is more intricate than traditional methods. Some manufacturers struggle with high initial investments. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh these drawbacks. Design engineers who embrace flexibility may achieve significant advances. Innovations in design and assembly techniques are continually evolving. Balancing cost with functionality remains a key consideration for many businesses.
Flexible printed circuit boards (Flex PCBs) have become essential in consumer electronics. These components offer significant advantages in design flexibility and space-saving capabilities. According to a report from Research and Markets, the global flexible PCB market is projected to reach $36.2 billion by 2027, driven by increased demand from various sectors, including consumer electronics.
In smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices, Flex PCBs enable complex designs in tight spaces. They can fold and conform, which allows manufacturers to maximize available real estate. For instance, Flex PCBs support multi-layer designs that can increase functionality without adding bulk. This adaptability enhances device performance while maintaining a sleek profile.
However, challenges exist. Manufacturing defects can occur more frequently in flexible boards compared to traditional rigid boards. Reliability can be a concern. Moreover, companies must invest in quality control processes and technology to minimize these risks. Balancing production costs with quality remains a persistent challenge in the industry. Integrating Flex PCBs into electronics is a double-edged sword; the benefits are clear, yet the road to perfection is often fraught with obstacles.
The assembly of flexible PCBs comes with unique challenges. The delicate nature of flexible materials requires precise handling. Tiny components can be difficult to place accurately, affecting the overall performance of the circuit. Misalignment issues are common, leading to potential failures during operation. The need for specialized equipment further complicates the production process.
Moreover, the testing phase can be quite demanding. Flex PCBs often require specific methods to ensure reliability. Standard testing procedures may not yield accurate results. Manufacturers must adapt their techniques to account for flexibility. This adaptation can increase production time and costs. Striking a balance between efficiency and reliability remains a key concern.
Overcoming these challenges may involve innovative solutions. Utilizing advanced alignment techniques can improve accuracy. Employing flexible adhesives might enhance component stability. Training personnel effectively is crucial as well; skilled workers can navigate complexities better. However, there’s still room for improvement in addressing these issues continuously.
| Dimension | Description | Challenges | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Ability to bend and twist in design. | Risk of mechanical failure. | Use of durable materials and proper stress testing. |
| Thickness | Varied thickness for adaptability. | Difficulty in manufacturing thin layers. | Advanced fabrication techniques. |
| Weight | Lightweight construction. | Potential for signal loss. | Optimization of circuit design and materials. |
| Customization | Tailored for specific applications. | Increased production time. | Efficient design processes and rapid prototyping. |
| Integration | Easy integration into existing systems. | Compatibility issues. | Comprehensive testing for integration compatibility. |
Flex PCB technology is gaining momentum in the electronics industry. Its adaptability allows for the design of unique shapes, which can fit into tight spaces. This flexibility is crucial for modern devices like smartphones and wearables. As electronics become more compact, the demand for flexible solutions grows alongside it. Designers and engineers are constantly exploring how to push the limits of traditional PCB designs.
Future trends indicate significant advancements in Flex PCB technology. Innovations in materials can enhance durability and thermal performance. These improvements make flex circuits suitable for high-performance applications. Additionally, manufacturers are focusing on automated assembly techniques. This can reduce production costs and improve consistency in quality. Yet, there are challenges, such as the need for more robust testing protocols. Designers must be cautious when adopting new technologies. Every innovation might bring potential risks that need thorough examination.